Returns properties of the symbols whose soids are specified here. The other-args argument names the properties to be returned.
Performs a sequence of resolve_next operations until the symbol is no longer undiscovered. If you apply this operation to a symbol that is not undiscovered, it returns the symbol itself.
Some symbols only serve to hold a reference to another symbol. For example, a typedef is a reference to the aliased type, or a const-qualified type is a reference to the non-consts qualified type. These reference types are called undiscovered symbols. This operation, when performed on an undiscovered symbol, returns the symbol the type refers to. When this is performed on a symbol, it returns the symbol itself.
address: the new address:
base_name: the new base name. The symbol must be a base name.
line_number: the new line number. The symbol must be a line number symbol.
loader_name: the new loader name and a file name.
scope: the soid of a new scope owner.
type_index: the new type index, in the form <n, m, p>. The symbol must be a type.
Sets a symbol’s property. Not all properties can be set. Determine which properties can be set using the writable_properties property. For example,
Arguments required by the get subcommand.
The TV::symbol command lets you examine and set the symbol properties and states.
Table 1 lists the properties associated with the symbols information that TotalView stores. Not all of this information will be useful when creating transformations. However, it is possible to come across some of these properties and this information will help you decide if you need to use it in your transformation. In general, the properties used in the transformation files that Rogue Wave Software provided will be the ones that you will use.
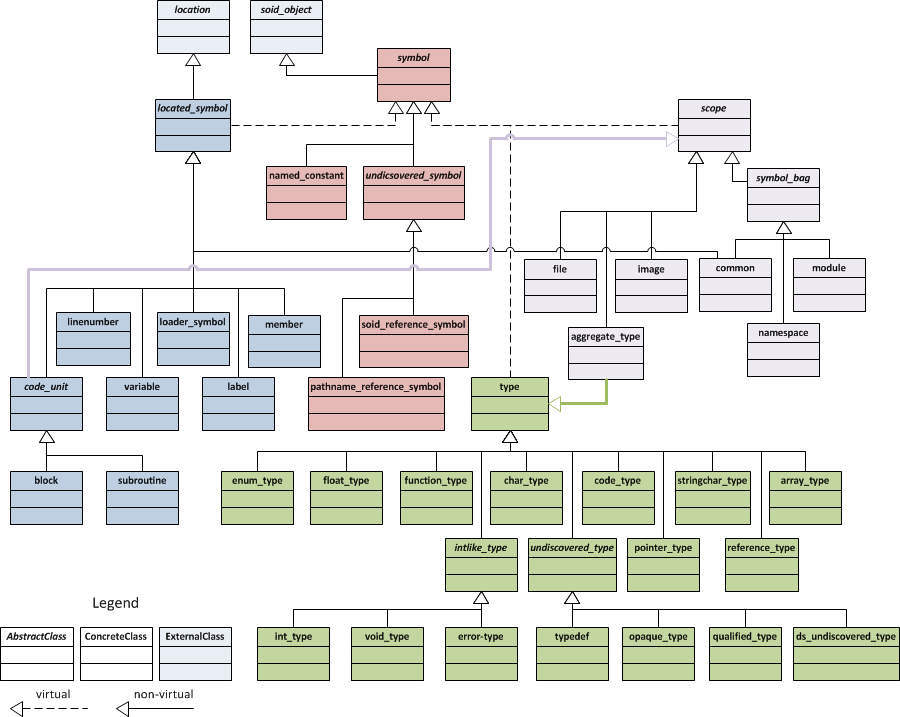
Figure 1 shows how these symbols are related.
|
Figure 1:
|
The compiler or family of compiler used to create the file; for example, gnu, xlc, intel, and so on.
Contains additional operands to get from the base of an object to its data; for example, a Fortran by-desc array contains a descriptor data structure. The variable points to the descriptor. If you do an addc operation on the descriptor, you can then do an indirect operation to locate the data.
|
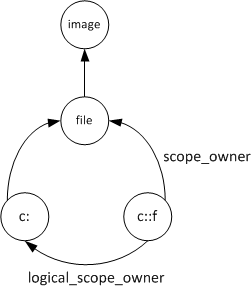
Figure 2:
|
Indicates if a symbol has been full or partially read-in. The following constants are or’d and returned: skim, index, line, and full.
Name of the enumerator tags. For example, if you have something like enum[R,G,B], the tags would be R, G, and B.
When used in data types, it translates the object structure to the type name for the language. For example, if you have a pointer that points to an int, the external name is int *.
This is the # separated static path to the variable; for example, ##image#file#externalname....
The array type’s index type_index; for example, this indicates if the index is a 16-, 32-, 64-bit, and so on.
For C++ variables, this string is as follows: [ virtual ] [ { private | protected | public } ] [ base class ]
The byte size of the object. For example, this might represent the size of an array or a subroutine.
|
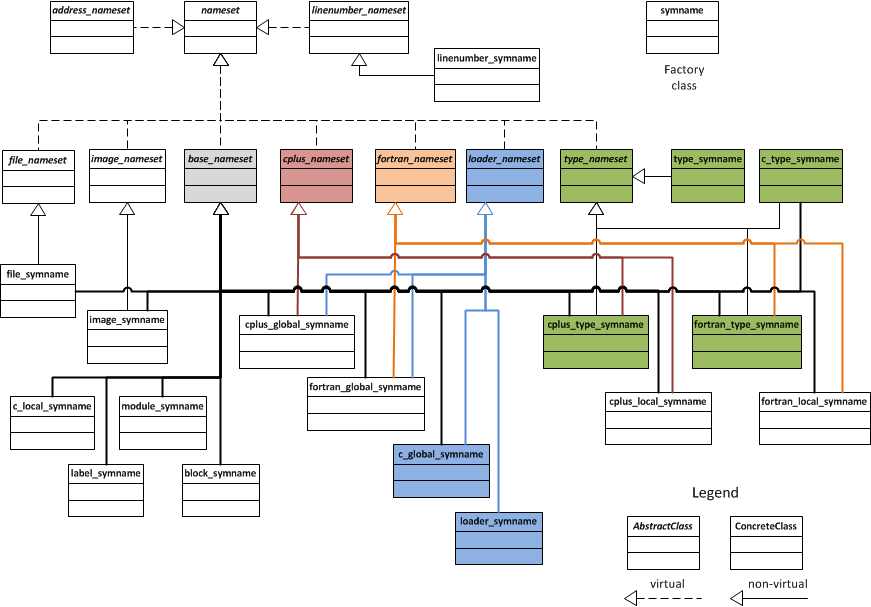
Figure 3:
|
A qualifier to a data type such as const or volatile. These can be chained together if there is more than one qualifier.
|
Figure 4:
|
The ID of the symbol’s scope owner. (This is illustrated by the figure within the logical_scope_owner definition.)
If you have an array of aggregates or pointers and you have already dived on it, this property gives you a list of {name type} tuples where name is the name of the member of the array (or * if it's an array of pointers), and type is the soid of the type that should be used to dive in all into that field.
The symbols described in the previous section all reside within namespaces. Like symbols, namespaces also have properties. Table 2 lists the properties associated with a namespace. Figure 5 illustrates how these namespaces are related.
|
Figure 5:
|
The parent of the subroutine. For example, the parent is module in a reference such as module‘subr. If you have an inner subroutine, the parent is the outer subroutine.
In a library, you might have an object reference; for example, libC.a(foo.so). foo.so is the member name.
A handle that points to the type definition. Its format is <number,number,number>.