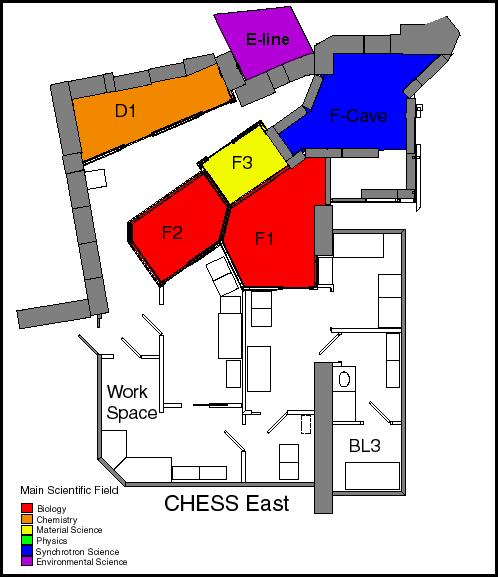
Click on the station names for more information
CHESS
East receives radiation from the positron beam in CESR.
Both F1
and F2
receive beam from the 24-pole East 1.2 T wiggler while the F3 station
gets x-rays from a CESR high-field dipole magnet. The F-cave area
was completely rebuilt in 1999 to upgrade the shielding levels and the
optics for F-line.
In addition, the F1/F2 area has been enclosed to provide a quieter and
more comfortable working environment.
F1 is
an experimental station in high demand, especially by the
macromolecular structure community. Doubly focused and tunable, it
delivers a tremendous x-ray flux onto small specimens. It was built
contiguous to a biohazard level 3 (BL3) safety facility, so that
certain classes of sensitive and potentially dangerous viruses can be
safely handled.
The F2
station has been in high demand by the macromolecular community for use
with the Multi-wavelength Anomalous Dispersion or MAD technique.
During the upgrade for F-line a new monochromator was built for the F2
station to better accommodate the needs of the users of this technique.
The F3
station has a sagittal Si(111) monochromator that provides horizontal
focusing of nearly 5 milliradians of hard-bend magnet radiation. The
station has been outfitted with a small Huber diffractometer and with
the enlargement of the station during the 1999 upgrade can better
accommodate a wide range of experiments. Two high resolution
analyzer crystal devices have been developed for the detector arm: one
is a standard analyzing crystal mount with motorized Bragg angle, and
the second has a special geometry for analyzing the polarization
content of the diffracted beam.
The E-line
is a new beam line that is presently being commissioned that is used
strictly for accelerator diagnostics. The beam line makes use of the
hard-bend radiation from a dipole between the D and F beam lines. There
is no experimental station associated with this beam line which is
located entirely in the accelerator shielding area. The beam from this
dipole is apertured horizontally to two beams. The Northern portion of
the beam is used to determine the vertical emittance of the positrons
and the Southern section for determining the horizontal emittance of
the positrons.
D-line
has been in high demand from users of the Materials Science, Chemistry,
Engineering, and Environmental Science communities for experiments
requiring high flux, but at a relaxed energy bandwidth. Recent
applications range from small-angle scattering and grazing-incidence
scattering to fluorescence imaging and ultrafast radiography.
Last Update:
2004-11-22