Steven Dutch, Natural and Applied Sciences, University of Wisconsin - Green
Bay
First-time Visitors: Please visit Site Map and Disclaimer. Use
"Back" to return here.
If we are only concerned about a single point, any symmetry is possible in two dimensions; a flower can have any number of petals. But if the pattern repeats, then the possibilities are very limited. Consider the diagram below:
o o o v q o o
\ /
a\ /a
o o u-----x-----p o
o o o o o o o
Point x is an axis of n-fold symmetry, and so is every other point. (The pattern repeats, after all.) So point u gets rotated to point v (among others), and point p gets rotated to point q. Now in this repeating pattern, all the points are spaced the same distance apart in the rows. Call that distance 1. Points v and q must be an integer distance apart. In the sketch they are distance 1 apart but in a square lattice, for example, they might coincide. Thus distance vq = an integer = 2 cos a
.
Now the cosine can only have values between -1 and 1, so 2 cos a, which must
be an integer, can only take on values -2, -1, 0, 1 and 2. Thus cos a can only
be -1, -1/2, 0, 1/2 and 1, or a = 180, 120, 90, 60 and 0 (or 360), respectively.
Since the rotations are symmetry rotations,
a = 360/n, so n = 2, 3, 4, 6, or
1
Thus, repeating patterns in the plane can only have 1, 2, 3, 4 or 6-fold symmetry. In particular, repeating patterns in the plane cannot have five-fold symmetry.
In the diagram below, points a, b, c, and d are symmetry axes (not necessarily the same kind in a plane pattern.
b
y | y
x | x
a-----------+-----------d
x | x
y | y
c
Symmetry axis a rotates b to c and vice versa. Axis b rotates a to d and so does axis c. Finally, axis d rotates b to c and vice versa. The rotated axes have to coincide eventually. If they do not, the entire plane will eventually be covered with an infinite number of symmetry axes. Apart from patterns with only one- and two-fold symmetry, the only possibilities are:
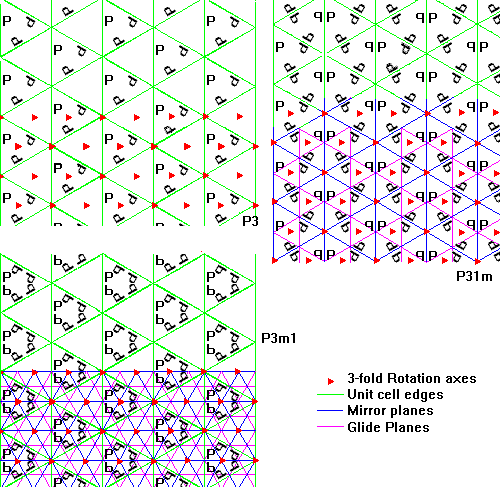
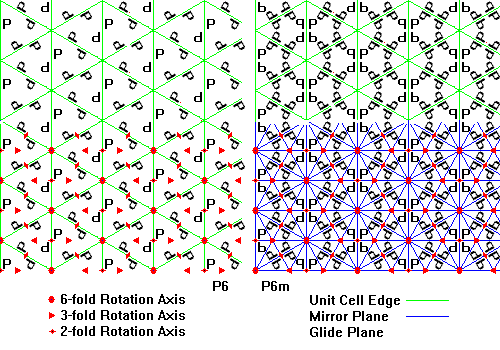
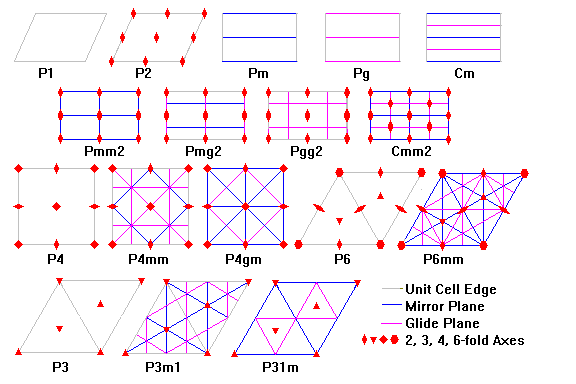
There are 17 space groups in the plane, but their unit cells fall into one of five basic shapes as follows:
+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+
/ / / / / /
/ / / / / /
/ / / / / /
--------+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+---
/ / / / / /
/ / / / / /
/ / / / / /
----+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+-------
/ / / / / /
/ / / / / /
/ / / / / /
+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+
+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+ | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | +-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+ | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | +-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+ | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | +-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+
+ + + + +-------+-------+-------+-------+----
/ \ / \ / \ / \ /|\ /|\ /|\ /| |
/ \ / \ / \ / \ / | \ / | \ / | \ / | |
/ \ / \ / \ / \ / | \ / | \ / | \ / | |
+ + + + + | + | + | + | + | +
\ / \ / \ / \ / \ | / \ | / \ | / \ | |
\ / \ / \ / \ / \ | / \ | / \ | / \ | |
\ / \ / \ / \ / \|/ \|/ \|/ \| |
+ + + + +-------+-------+-------+-------+----
/ \ / \ / \ / \ /|\ /|\ /|\ /| |
/ \ / \ / \ / \ / | \ / | \ / | \ / | |
/ \ / \ / \ / \ / | \ / | \ / | \ / | |
+ + + + + | + | + | + | + | +
\ / \ / \ / \ / \ | / \ | / \ | / \ | |
\ / \ / \ / \ / \ | / \ | / \ | / \ | |
\ / \ / \ / \ / \|/ \|/ \|/ \| |
+ + + + +-------+-------+-------+-------+----
The simplest unit cell for this pattern is a rhombus, but the pattern also has a rectangular structure. To bring out the rectangular pattern, this lattice is often described as a rectangle with an extra point in the center. Such a lattice is called centered.
+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+ | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | +-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+ | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | +-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+ | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | +-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+-------+
+ + + + + + + + +-----+-----+-----+---
/ / / /
/ / / /
+ + + + + + + + +-----+-----+-----+-----+
\ / \ / \ / \ /
\ / \ / \ / \ /
+ + + + + + + + + + + +
/ \ / \ / \ / \
/ \ / \ / \ / \
+ + + + + + + + + + + + +
\ / \ / \ / \ /
\ / \ / \ / \ /
+ + + + + + + + +-----+-----+-----+---
\ \ \ \
\ \ \ \
+ + + + + + + + + +-----+-----+-----+
Note that there are three equivalent ways to orient the unit cells.
+ + + + + + + + + + + +
p p p p p p p p p p p p
+ + + + + + + + + + + +
p p p p p p p p p p p p
+ + + + + + + + + + +
p p p p p p p p p p p
+ + + + + + + + + + + +
d d d d d d
+ + + + + + + + + + +
p p p p p p
+ + + + + + + + + + + +
d d d d d d
+ + + + + + + + + + +
p p p p p p
+ + + + + + + + + + + +
There are 2-fold axes at the + locations.
p p p p p p p p p p p
---------------------------------------------------------------------
b b b b b b b b b b b
---------------------------------------------------------------------
p p p p p p p p p p p
---------------------------------------------------------------------
b b b b b b b b b b b
---------------------------------------------------------------------
p p p p p p p p p p p
---------------------------------------------------------------------
b b b b b b b b b b b
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Parallel mirror planes
p p p p p p p p p p p
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
b b b b b b b b b b b
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
p p p p p p p p p p p
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
b b b b b b b b b b b
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
p p p p p p p p p p p
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
b b b b b b b b b b b
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Parallel glide planes
+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+ |p | q|p | q|p | q|p | q|p | q|p | q| +-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+ |b | d|b | d|b | d|b | d|b | d|b | d| +-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+ |p | q|p | q|p | q|p | q|p | q|p | q| +-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+ |b | d|b | d|b | d|b | d|b | d|b | d| +-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+ |p | q|p | q|p | q|p | q|p | q|p | q| +-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+-----+
Perpendicular mirror planes
+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+ |p | q|p | q|p | q|p | q|p | q|p | q| +- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+ | d|b | d|b | d|b | d|b | d|b | d|b | +- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+ |p | q|p | q|p | q|p | q|p | q|p | q| +- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+ | d|b | d|b | d|b | d|b | d|b | d|b | +- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+ |p | q|p | q|p | q|p | q|p | q|p | q| +- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+
Perpendicular mirror and glide planes
+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+ |p d| |p d| |p d| |p d| |p d| |p d| | +- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+ | |b q| |b q| |b q| |b q| |b q| |b q| +- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+ |p d| |p d| |p d| |p d| |p d| |p d| | +- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+ | |b q| |b q| |b q| |b q| |b q| |b q| +- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+ |p d| |p d| |p d| |p d| |p d| |p d| | +- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+ | |b q| |b q| |b q| |b q| |b q| |b q| +- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+- - -+
Perpendicular glide planes. (p,b) and (d,q) are related by horizontal glides, (p,q) and (b,d) by vertical glides. Note that the intersections of the glide planes and the centers of the boxes outlined by the glide planes are also two-fold symmetry axes.
p p p p p p p p p p p
---------------------------------------------------------------------
b b b b b b b b b b b
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
p p p p p p p p p p p p
---------------------------------------------------------------------
b b b b b b b b b b b b
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
p p p p p p p p p p p
---------------------------------------------------------------------
b b b b b b b b b b b
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
p p p p p p p p p p p p
---------------------------------------------------------------------
b b b b b b b b b b b b
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Parallel mirror and glide planes. The pattern of stars on a 50-star flag has this symmetry.
+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+ |p : | q|p : | : q|p : | : q|p : | : q|p : | : q|p : | : q| +--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+ |b : | : d|b : | : d|b : | : d|b : | : d|b : | : d|b : | : d| + -:- + -:- + -:- + -:- + -:- + -:- + -:- + -:- + -:- + -:- + -:- + -:- + | : q|p : | : q|p : | : q|p : | : q|p : | : q|p : | : q|p : | +--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+ | : d|b : | : d|b : | : d|b : | : d|b : | : d|b : | : d|b : | + -:- + -:- + -:- + -:- + -:- + -:- + -:- + -:- + -:- + -:- + -:- + -:- + |p : | : q|p : | : q|p : | : q|p : | : q|p : | : q|p : | : q| +--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+ |b : | : d|b : | : d|b : | : d|b : | : d|b : | : d|b : | : d| + -:- + -:- + -:- + -:- + -:- + -:- + -:- + -:- + -:- + -:- + -:- + -:- + | : q|p : | : q|p : | : q|p : | : q|p : | : q|p : | : q|p : | +--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+--:--+
Alternating mirror and glide planes in both directions. All intersections are also two-fold symmetry axes. Bricks in a wall have this symmetry.

Return to Symmetry
Index
Return to Crustal
Materials Index
Return to
Professor Dutch's Home page
Created 17 Sep 1997, Last Update 22 Sep 1999
Not an official UW Green Bay site