EventStore project
was designed to replace existing data access model based
on
Objectivity DB
for
CLEO-c collaboration.
The EventStore handles efficiently and reliably the
data coming from CLEO detector. We expect to store around 200TB of data by
2008.
The EventStore developed to work on the following platforms:
- SunOS 2.6 and Solaris 2.8, 9, 10
- Linux, RedHat 9, RedHat Enterprise 3, 4, Scientific Linux
and supports various DB backends:
- SQLite
- MySQL
- we plan to use DB2 or ORACLE at peak of data taking
Short summary:
- support various file formats, including raw (binary) and PDS.
- handle raw, reconstructed and MonteCarlo data
- allow various data access patterns, including MetaData access
- data versioning and reproducability
- reliable and fault tolerant data access (multiple DB servers, interaction with HSM)
- fast data access and readback
- multiple DB backends (SQLite, MySQL), additional plugins can be easily added
For full list, please visit this
page.
SQLite DB doesn't support nested transactions. Load balancing for data access
is required.
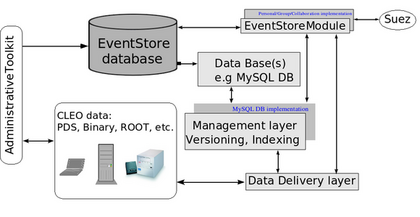
To fullfill our goal we decided to index data and store
navigation information
for data access into a backend database.
The data themselves can reside elsewhere: on tape, disk servers or user desktops/laptops.
As shown in figure, a client application
suez uses EventStore to provide
access to data through various layers. A three major ones are DB, Management and data
delivery layer. A separate toolkit has been used to feed EventStore DB.
Full implementation was done in C++ for the client code and in Python for
administrative toolkit. We achieved a good performance of reading
data at the level of 20K events/second on Linux 1GHz/512MB platform.
The details of this work has been published in
CHEP'04
(
PDF )
and
DPF'04
(
PDF)
conference proccedings, slides from my talk at DPF available
here.