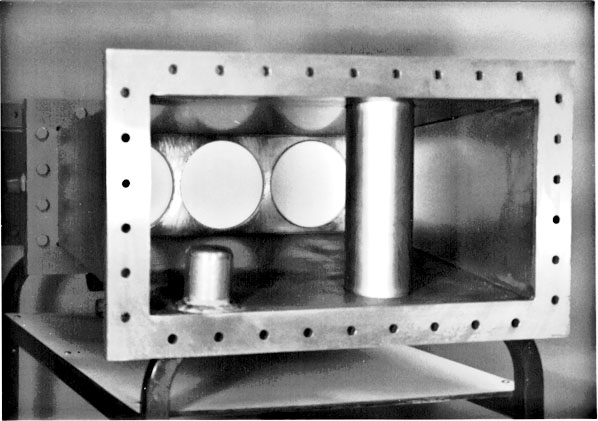
Suprconducting RF for CESR
The CESR Luminosity Upgrade Plan consists of several consecutive steps, or phases [1-3]. At present time, this program is in Phase III, designed to yield a luminosity of 1.7x10^33 cm^-2 sec^-1 with 45 bunches in each beam for a total current of 1 A . This plan utilizes four superconducting single-cell cavities with an accelerating gradient of 6 to 10 MV/m , which corresponds to a peak accelerating voltage of 1.8 to 3 MV per cell. The power transferred to the beam by each cavity would be 325 kW . The use of only four SRF cells with stronger damped higher-order modes (HOMs), as compared to the old twenty normal-conducting copper cells, decreases both the broad and narrow band impedances sufficiently to allow stable operation at the high current level [4-5]. Each SRF cavity has its individual cryostat, input coupler and RF window, two ferrite HOM loads, taper transition(s) to the adjacent CESR beam tube, and some other beam-line components. The name BB1 has been assigned to the Cornell superconducting 500 MHz single-cell cavity shape. Five cavities have been manufactured to date: the first, BB1-1, by Dornier, all others, BB1-2 through BB1-5, by ACCEL . The BB1-1 cavity [6] and prototypes of RF window [7], cryostat [8], HOM loads [10, 19] and beam line components were subjected to a successful beam test in CESR in August 1994 [9-11]. After that necessary changes were made to the design of some components, the new, MARK II cryostat * was designed to meet a rather tight space requirements of the CESR tunnel, and the cavity was equipped with the new ceramic RF window [12, 15-16]. The design and layout of the new RF system was thus completed [13-14].Beam line components subject to 1994 CESR test
References
- D. L. Rubin. CESR Status and Plans. In Proceedings of the 1995 Particle Accelerator Conference, 1, 481-485.
- D. Rice. CESR: Steps toward a B-factory. In Proceedings of the Fifth European Particle Accelerator Conference, 17-21.
- S. B. Peck and D. L. Rubin. CESR Performance and Upgrade Status. In Proceedings of the 1999 Particle Accelerator Conference, in print.
- H. Padamsee, et al. Design Challenges for High Current Storage Rings. Particle Accelerators, 40 , 17-41 (1992).
- J. Kirchgessner. The Use of Superconducting RF for High Current Applications. Particle Accelerators, 46 , 151-162 (1994).
- D. Moffat, et al. Preparation and Testing of a Superconducting Cavity for CESR-B. In Proceedings of the 1993 Particle Accelerator Conference, 763-765.
- D. Metzger, et al. Test Results and Design Considerations for a 500 MHz, 500 kWatt Vacuum Window for CESR-B. In Proceedings of the 1993 Particle Accelerator Conference, 1399-1401.
- E. Nordberg, et al. Cryostat for a Beam Test with the CESR-B Cavity. In Proceedings of the 1993 Particle Accelerator Conference, 995-997.
- H. Padamsee, et al. Beam Test of a Superconducting Cavity for the CESR Luminosity Upgrade. In Proceedings of the 1995 Particle Accelerator Conference, 3 , 1515-1517.
- S. Belomestnykh, et al. Comparison of the Predicted and Measured Loss Factor of the Superconducting Cavity Assembly for the CESR Upgrade. In Proceedings of the 1995 Particle Accelerator Conference, 5 , 3394-3396.
- S. Belomestnykh, et al. Wake fields and HOMs Studies of a Superconducting Cavity Module with the CESR beam. In Proceedings of the 1995 Particle Accelerator Conference, 5 , 3391-3393.
- M. Pisharody, et al. High Power Window Tests on a 500 MHz Planar Waveguide Window for the CESR Upgrade. In Proceedings of the 1995 Particle Accelerator Conference, 1720-1722.
- S. Belomestnykh, et al. Superconducting RF System for the CESR Luminosity Upgrade: Design, Status, and Plans. In Proceedings of the Fifth European Particle Accelerator Conference, 2100-2102 (1996).
- S. Belomestnykh, et al. Development of Superconducting RF for CESR. In Proceedings of the 1997 Particle Accelerator Conference, 3 , 3075-3077.
- E. Chojnacki, et al. Design of a High Average Power Waveguide Window. In Proceedings of the 1997 Particle Accelerator Conference, ?-?.
- E. Chojnacki, et al. Tests and Designs of High-power Waveguide Vacuum Window at Cornell. Particle Accelerators, 61 [309-319]/45-55 (1998).
- S. Belomestnykh, et al. Commissioning of the Superconducting RF Cavities for the CESR Luminosity Upgrade. In Proceedings of the 1999 Particle Accelerator Conference, in print.
- S. Belomestnykh. The High Luminosity Performance of CESR with the New Generation Superconducting Cavities. In Proceedings of the 1999 Particle Accelerator Conference, in print.
- E. Cojnacki, et al. Beamline RF Load Development at Cornell. In Proceedings of the 1999 Particle Accelerator Conference, in print.
- R. Geng and H. Padamsee. Condensation/Adsorption and Evacuation of Residual Gases in the SRF System for the CESR Luminosity Upgrade. In Proceedings of the 1999 Particle Accelerator Conference, in print.
- R. Geng and H. Padamsee. Exploring Multipacting Characteristics of a Rectangular Waveguide. In Proceedings of the 1999 Particle Accelerator Conference, in print.
- E. Cojnacki and J. Sears. Superconducting RF Cavities and Cryogenics for the CESR III Upgrade. In Proceedings of the 1999 Cryogenic Engineering and International Cryogenic Materials Conference, in print.
- To watch a movie of the MARK II cryostat assembly , download Final_Movie.avi file (49 MB).