P3318: Analytical Mechanics
Instructor: Veit Elser.
Section: Friday 2:30-3:20pm, Rockefeller 102.
Office Hours: Mon 5:15-6:15pm, PSB 425G or by appointment.
Announcement: Congrats on surviving the course!
This is a collection of course material related to the course P3318: Analytical Mechanics at Cornell University. I was the TA in Winter 2013 under Veit Elser. See also the main course website.
Course data
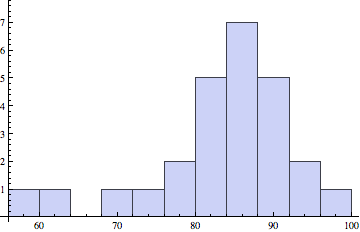
Cumulative course grade, modified HW grade
Based on: 35% homework, 20% prelim 1, 20% prelim 2, 25% final
Modified homework grade: drop lowest score
Course grade (left): Median, Mean (Std. Dev): 85.9, 83.8 (9.3)
Modified HW (right): Median, Mean (Std. Dev): 87.2, 83.8 (14.1)
Remark: grades will be based on weighted sum of z-scores*, perhaps accounting for outliers.
*-z-score: shifted and rescaled data such that mean = 0 and variance = 1
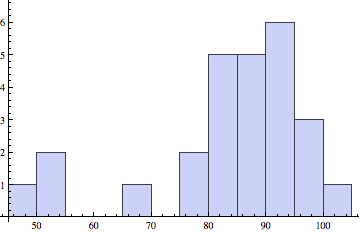
Final exam and raw homework grades
HW based on 10 assignments, 10 points each.
Final (left): Median, Mean (Std. Dev): 87, 86.3 (10.1)
Final exam solutions by Prof. Elser
Raw HW (right): Median, Mean (Std. Dev): 87, 84.1 (15.4)
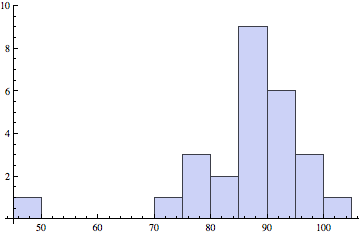
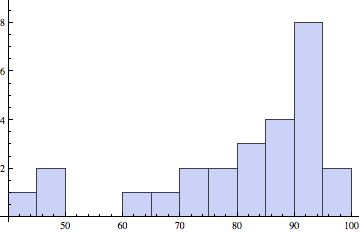
Prelim scores
Prelim 2 (left): Median, Mean (Std. Dev): 82.5, 81.1 (17.9)
Prelim 1 (right): Median, Mean (Std. Dev): 87, 84.7 (18.0)
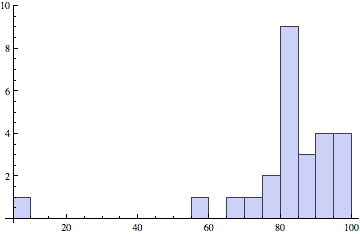
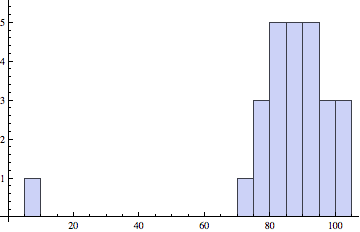
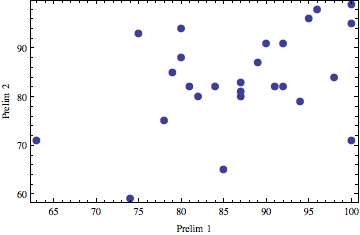
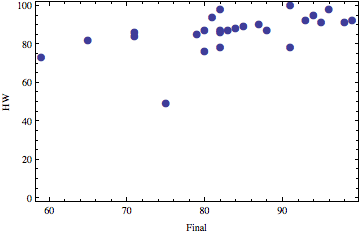
Correlations
Left: prelim 1 and prelim 2, right: final and HW.
Homework and exam solutions
Includes problems.
- HW 1: Degrees of freedom, Lagrangians, scaling
- HW 2: More fun with Lagrangians, equations of motion
- HW 3: Variational principle
- HW 4: Central force motion
- Prelim 1
- HW 5: Gravitational 2-body problem
- HW 6: Hamiltonian Mechanics (see
addendum)
- HW 7: Dynamics of phase space
- Prelim 2
- HW 8: Dynamics of phase space, rotations
- HW 9: Rotations, moment of inertia (solutions courtesy of Clara Peset), see final review notes for another take on the Larmor precession problem
- HW 10: The symmetric top, see this image for another take on the relation between the tubeworld psi and theta angles.
Lecture notes
Professor Elser's lecture notes.
- Lec 1: Symmetry, variational principles, phase space
- Lec 2: Degrees of freedom, generalized coordinates, generalized velocities, generalized forces
- Lec 3: Kinetic energy, conservative forces, the Lagrangian
- Lec 4: Equations of Motion, the Hamiltonian, H vs. E
- Lec 5: Conjugate momentum, non-holonomic constraints
- Lec: Non-holonomic constraints
- Lec 6: Non-holonomic constraints, Brachistochrone, calculus of variations
- Lec 7: Calculus of variations and mechanics
- Lec 8: Extensions of variational calculus
- Lec: Constrained variations
- Lec: Classical mechanics as a limit of quantum
- Lec: The two-body problem
- Lec: Gravitational orbits
- Lec: Gravitational 2-body problem I
- Lec: Gravitational 2-body problem II
- Lec: Gravitational 2-body problem III
- Lec: Noether's theorem
- Lec: The Hamiltonian formalism
- Lec: Dynamics on Phase Space I: Liouville's theorem
- Lec: Dynamics on Phase Space II: Consequences of Liouville's theorem
- Lec: Dynamics on Phase Space III: Poincare recurrence, action principle in phase space
- Lec: Dynamics on Phase Space IV: canonical transformation, Poisson bracket, generating functions
- Lec: Dynamics on Phase Space V: generating functions
- Lec: Dynamics on Phase Space V: four types of generating functions, action-angle variables
- Lec: Adiabatic variation of the pendulum
- Lec: Applications of Adiabatic invariance: the Levitron, atom traps
- Lec: Kinematics in rotating frames I: body vs. space, rotation matrices, time-dependent rotations and instantaneous angular velocity, open dot time derivative
- Lec: Kinematics in rotating frames II: fictitious forces, Foucault pendulum.
- Lec: Dynamics in rotating frames: kinetic energy
- Lec: Free precession of a rigid body, Euler's equations, symmetric top, football wobble
- Lec: The big picture: connection to quantum and statistical mechanics.
Section notes
- Section 1: Degrees of Freedom in extra dimensions, Dog on the beach (and relation to quantum mechanics), Dimensional analysis for allometry
- Section 2: Indices, ugly integrals, velocity-dependent forces, brief remarks on geometry
- Section 3: The Lagrangian is smarter than us, constraints, variational calculus
- Section 4: The big picture; harmonic oscillator
- Section 5: prelim review
- Section 5 addendum: non-holonomic constraints
- Section 5.5: prelim 1 debriefing
- Section 6: cancelled, see examples in lecture
- Section 7: open office hours (Dragon Day), see Prof. Elser's notes
- Section 8: generating functions for canonical transformations (useful for homework)
- Section 9: prelim review
- Section 10: prelim 2 debriefing
- Section 11: The falling cat, part I. For more, see David Tong's lectures.
- Section 12: The moment of inertia tensor, the falling cat part II. We closed by talking about the some relations to geometry, see Robert Batterman's notes.
- Cornell SPS talk, by request: What does all the formalism of classical mechanics buy us? A peek at some current topics in particle theory. (Caveat: a very biased view!)
- Final review: The moment of inertia
- Final exam: solutions by Prof. Elser

Image courtesy of Mandy Guo
Substitute lectures
Flip's personal notes, based on Prof. Elser's notes above.
- 2/18: The two body problem
- 3/4: Gravitational potentials, part III
- 3/6: Noether's theorem
- 3/8: Hamilton's equations
- 3/24: Foucault pendulum
References
Here are a few additional references that you might enjoy reading.